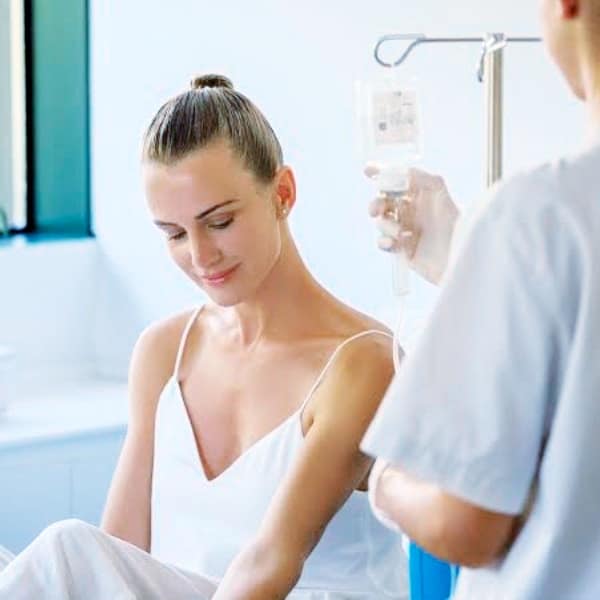
Ozon Theraphy
What is Ozone?
Ozone is a colorless, sharp-smelling gas consisting of three oxygen atoms found naturally in the environment. It exists in a gaseous state in nature. It is a potent disinfectant, antimicrobial, immune system regulator, and antioxidant.
History
- Ozone was discovered in 1840 by Austrian chemist Christian Schönbein.
- During World War I, Dr. Albert Wolff applied ozone therapy to German soldiers with severe injuries such as gangrene.
- In 1995, the US Department of Health approved ozone therapy as a complementary medical practice. Subsequently, clinical and academic studies rapidly increased, and ozone therapy began to be widely applied in the field of medicine worldwide.
- In Turkey, it was recognized as a complementary medicine practice by Regulation No. 29158 published in the Official Gazette on October 27, 2014.
- To apply medical ozone therapy, an ozone-oxygen mixture is obtained with the help of a generator from pure oxygen.
Benefits of Ozone Therapy
It is effective against bacteria, viruses, and fungi, similar to antibiotics. This includes the most recent viral diseases such as influenza, SARS, MERS, and COVID-19. Regulates the immune system and helps strengthen the autoimmune system in treatment. Speeds up metabolism. Regulates circulation and plays a significant supportive role in the treatment of coagulation disorders. Increases the body’s oxygen capacity, allowing all cells to function better. Treats pain in muscle tissues. Regulates the functions of the reproductive system.
How Is Ozone Therapy Applied?
- Blood Application (Major Application): During the procedure, the collected blood is oxygenated with ozone and then reintroduced to the individual through a vein. The therapeutic effects of ozone interacting with blood cells begin upon entering the body. In each session, a vein is opened, and the blood is placed in an ozone-resistant glass bottle and reintroduced into the body with ozone-resistant materials.
- Rectal Application: This is the application of ozone gas in the rectal area, similar to suppository applications. By promoting the multiplication of beneficial bacteria and reducing harmful bacteria in the intestines, it regulates digestive system functions. Like blood application, it has the same effectiveness and can be safely used in individuals where a vein cannot be opened, in babies, and children.
- Ozone Vaccine Application (Minor Application): Ozonated 2-5 ml blood drawn with a special ozone-resistant injector is injected into the muscle. It strengthens the immune system, especially during the winter months.
- Intra-Articular Ozone Application: Intra-articular ozone therapy applied inside the joint is effective in reducing knee pain in cases of meniscus, knee osteoarthritis, and chronic knee pain.
- Local Ozone Application: It is used for muscle pain, back pain, neck pain, and regional slimming purposes using micro-needles.
FAQs
How Many Treatment Sessions Should I Get?
The number of ozone therapy sessions and the dose of ozone to be applied are determined by the physician based on the patient’s age, overall condition, and the specific condition being treated. Ozonotherapy sessions are generally recommended to be administered 1-3 times per week.
For recovery, 8-12 sessions are typically recommended. After the first 4 sessions, individuals experience increased sleep and the body enters a repair phase. Starting from the 8th session, the antioxidant defense mechanism becomes active, and patients generally feel more energetic.
Diseases with High Success in Ozonotherapy When Applied Alone
Ozone therapy can be applied as a complementary treatment to modern medicine or as an independent treatment. Below are some of the conditions in which ozone therapy has been found to be highly successful:
- Chronic fatigue syndrome and fibromyalgia.
- Infectious diseases such as influenza, SARS, MERS, COVID-19, hepatitis, HIV, herpetic infections, herpes zoster, papillomavirus infections, onychomycosis, and candida infections, among others.
- Osteomyelitis, pleural empyema, fistulas, abscesses, infected wounds, bedsores, chronic ulcers, diabetic foot ulcers, and burns.
- Advanced ischemic diseases.
- Age-related macular degeneration (atrophic form).
- Localized osteoarthritis.
- Primary tooth root decay, especially in children.
- Recurrent or chronic infections of the oral cavity.
- Bartolin and vaginal candida infections.
- Especially antibiotic and chemoresistant bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Acute and chronic infections.
Remarkable Results Achieved with Ozone Therapy
Ozone therapy has shown remarkable results in various conditions, including:
- Cancer-Related Fatigue: Ozone therapy has been shown to improve cancer-related fatigue and enhance the quality of life for patients undergoing chemotherapy and radiation therapy. However, there is not yet sufficient data to support its use as a primary treatment for cancer.
- Asthma: While ozone therapy can provide excellent results for some patients with asthma due to its multifactorial nature, it may not be equally effective for all individuals with this condition.
Diseases Where Success Increases When Used as a Support for Modern Treatment
Ozone therapy can be highly effective as a complementary treatment for various conditions, including:
- Autoimmune Diseases (Multiple Sclerosis, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Crohn’s Disease, Ulcerative Colitis, Psoriasis): Ozone therapy may support the management of autoimmune diseases and reduce symptoms when used alongside conventional treatments.
- Senile Dementia: Ozone therapy might offer benefits in the management of senile dementia, a type of age-related cognitive decline.
- Pulmonary Diseases (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis): When combined with modern treatments, ozone therapy can be supportive in the management of pulmonary diseases.
- Skin Diseases (Psoriasis, Atopic Dermatitis): Ozone therapy may be a helpful adjunct therapy for skin conditions like psoriasis and atopic dermatitis.
- Metastatic Cancer: In some cases, ozone therapy is considered as a complementary approach to support conventional treatments in the management of metastatic cancer.
- Sepsis: Ozone therapy has been explored as a supportive therapy in the management of sepsis, a severe and often life-threatening condition resulting from infection.
It’s important to note that the use of ozone therapy as a complementary treatment should be under the supervision of qualified medical professionals and integrated into a patient’s overall treatment plan. The effectiveness of ozone therapy can vary depending on the specific condition and the individual patient’s response to treatment.
Who are not suitable for Ozone Therapy?
Ozone therapy is considered safe and a natural treatment approach with minimal side effects when administered correctly. However, there are certain conditions in which ozone therapy is not recommended, including:
- G6PD (Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase) Deficiency – Favism: Individuals with G6PD enzyme deficiency, a genetic condition that can lead to hemolytic anemia, should avoid ozone therapy. This condition is sometimes triggered by substances found in fava beans, and ozone therapy could potentially exacerbate it.
- During Hyperthyroidism (Excessive Thyroid Hormone Levels): Ozone therapy should be avoided during the active phase of hyperthyroidism when thyroid hormone levels are significantly elevated.
- Advanced Anemia, Bleeding Disorders, and Coagulation Abnormalities: Individuals with severe anemia, bleeding tendencies, or significant coagulation disorders should not undergo ozone therapy, as it may exacerbate these conditions.
- Chronic and Recurrent Pancreatitis: Ozone therapy may not be recommended for individuals with chronic and recurrent pancreatitis, as it could potentially worsen the condition.
- Recent Myocardial Infarction (Heart Attack) and Acute Stroke: Ozone therapy is generally avoided in individuals who have experienced a recent heart attack or acute stroke.
It’s crucial for individuals considering ozone therapy to consult with a qualified healthcare provider to assess whether the treatment is suitable for their specific health condition and medical history. Ozone therapy should always be administered under the guidance and supervision of trained medical professionals.
Any side effects?
Ozone gas can indeed be toxic when inhaled directly, and it has the potential to irritate the eyes and respiratory passages. Therefore, precautions should be taken to ensure that it is not present in the surrounding environment. Ozone therapy, as a medical treatment, is administered in a controlled and precise manner, typically not involving direct inhalation of ozone gas to avoid these adverse effects.